
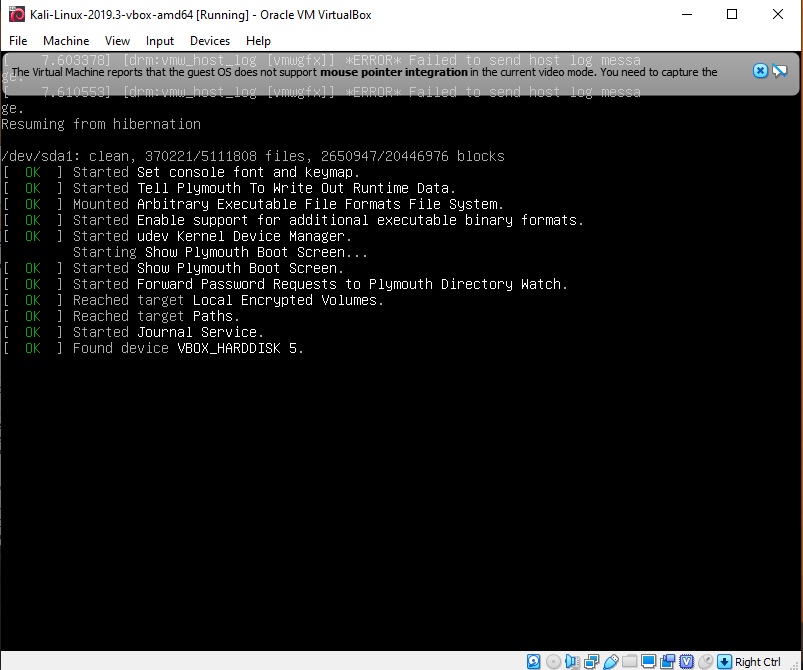
- #KALI LINUX VIRTUALBOX INSTALL DEFAULT USERNAME AND PASSWORD HOW TO#
- #KALI LINUX VIRTUALBOX INSTALL DEFAULT USERNAME AND PASSWORD MOD#
- #KALI LINUX VIRTUALBOX INSTALL DEFAULT USERNAME AND PASSWORD MANUAL#
#KALI LINUX VIRTUALBOX INSTALL DEFAULT USERNAME AND PASSWORD MOD#
So, I cannot mod users, modify the sudoers file, update, or just about anything without the root password (see first note above.) So, my one and only user no longer has admin privs and/or cannot access sudo because of this file. Unfortunately I forgot to include the ‘admin’ group in the -g list, thereby (and I am assuming here) I was removed (?) from the sudoers file. So, here’s the deal: I did a moduser and changed my groups. Having personally worked with Unix for over 25 years, I find my situation infuriating to say the least. Let me say this: This assumption that Ubuntu makes in limiting access using what amounts of vague commands to the novice user is redundant, as the novice user doesn’t know anything about the vague commands of Unix, Linux, etc. 🥺 Was this helpful? Please add a comment to show your appreciation or feedback ↓īelieve it or not, this is a rather annoying issue. Join the nixCraft community via RSS Feed, Email Newsletter or follow on Twitter. He wrote more than 7k+ posts and helped numerous readers to master IT topics. Vivek Gite is the founder of nixCraft, the oldest running blog about Linux and open source.
#KALI LINUX VIRTUALBOX INSTALL DEFAULT USERNAME AND PASSWORD HOW TO#

Supply your password and you will become a root user. Open the terminal application and simply type the following sudo command
#KALI LINUX VIRTUALBOX INSTALL DEFAULT USERNAME AND PASSWORD MANUAL#
Note that most shells behave differently when a command is specified as compared to an interactive session consult the shell’s manual for details. If no command is specified, an interactive shell is executed. If a command is specified, it is passed to the shell for execution via the shell’s -c option.
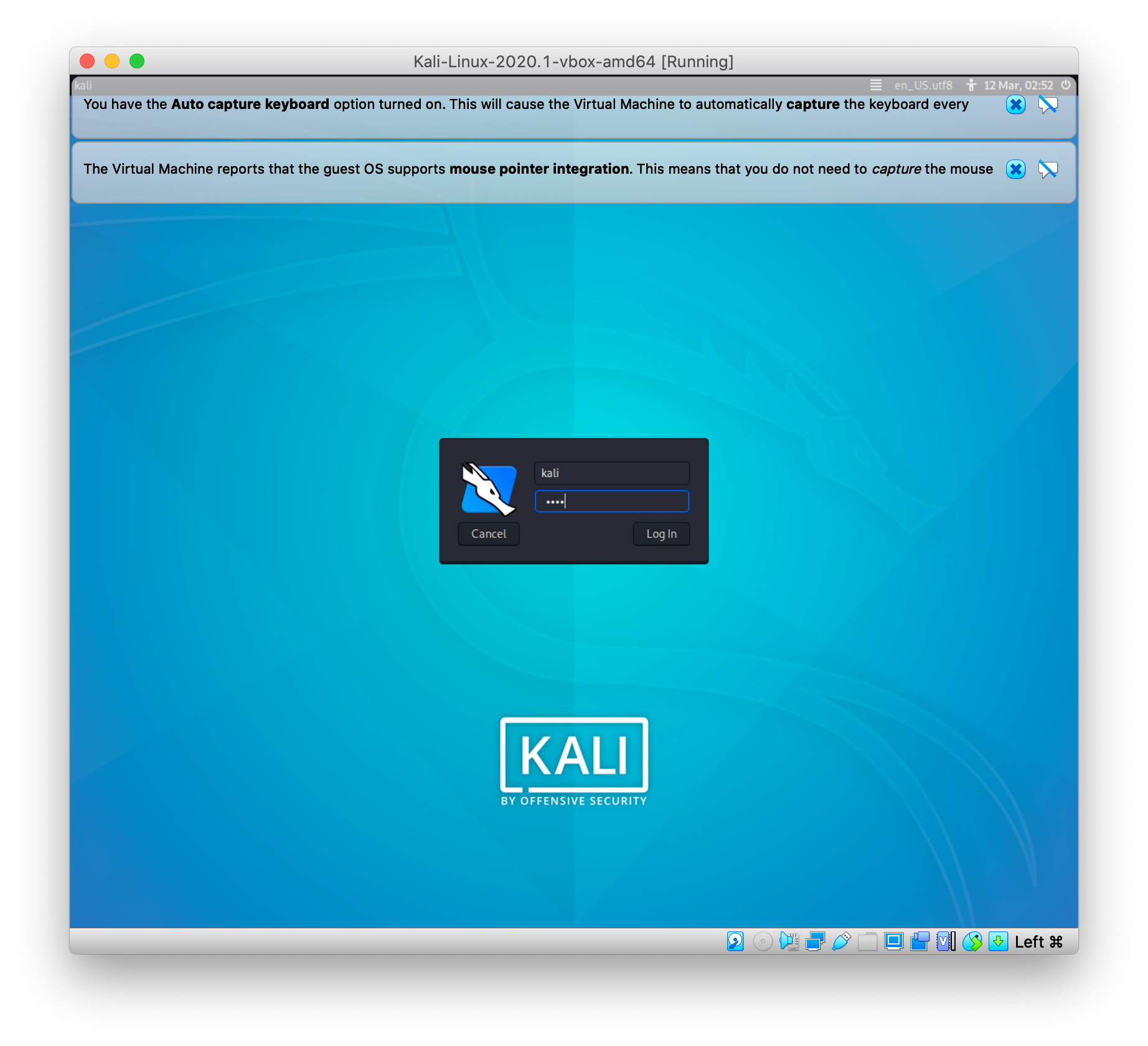
This means that login-specific resource files such as. -i : Run the shell specified by the target user’s password database entry as a login shell.Where, sudo command options are as follows: Note that this is not recommended until and unless you are an expert and aware of what you are typing or doing:Ībove command will start /bin/bash as a root shell so that you can enter a root user command without using sudo command.
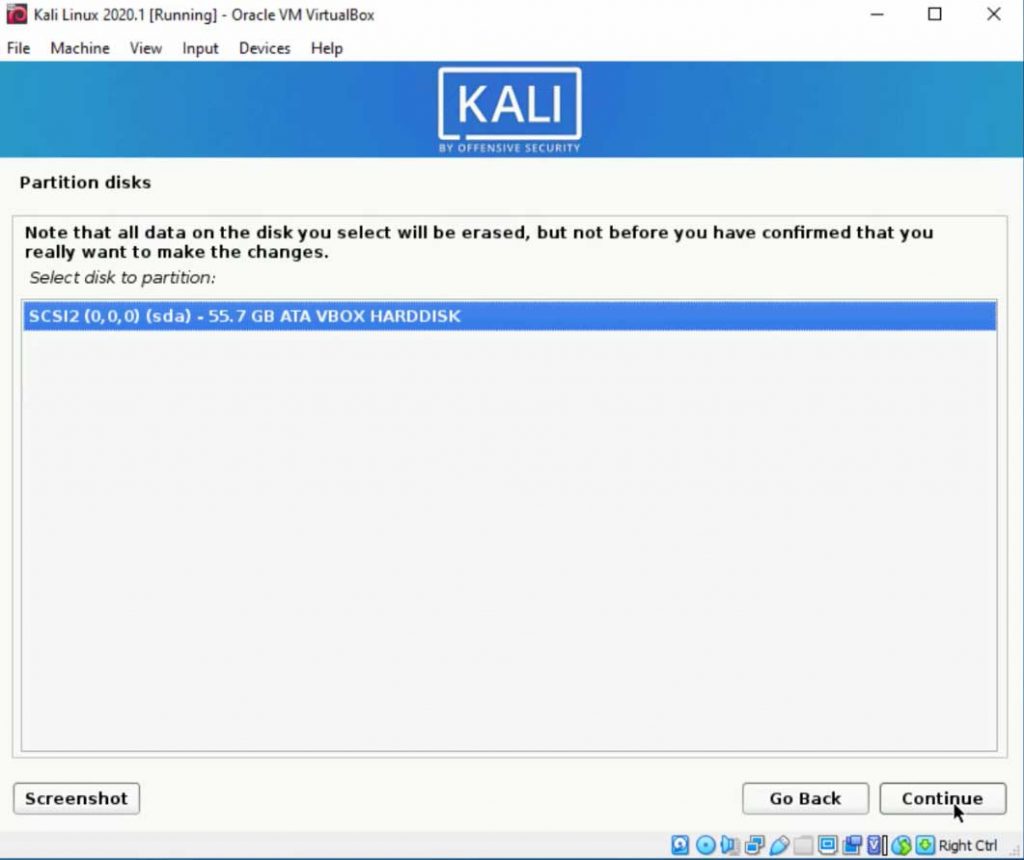
$ sudo systemctl restart ssh Avoid typing sudo each and every time on Ubuntu Linux Start / stop / restart services stored in /etc/init.d/ directory In other words a root password is not needed. When sudo asks for a password, you need to supply YOUR OWN password. For example create a new user called bar, you need to type sudo command as follows: Ubuntu setup your default account (the one created during installation) to run all administrative commands. sudo allows a permitted user to execute a command as the superuser or another user. To run all administrative command use the sudo command on Ubuntu. Therefore, you cannot log in as root or use ‘su -‘ command to become a superuser. By default root account is locked under Ubuntu Linux.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
